How to Make Molds for Metal Casting?
Metal casting is one of the oldest and most widely used manufacturing processes, allowing molten metal to be shaped into complex and precise parts. At the heart of every successful metal casting process is a properly made mold.
This guide explains how to make molds for metal casting, covering the most common mold-making methods, materials, and workflows used in modern foundries, jewelry production, and small-scale manufacturing.
1. What Is a Mold in Metal Casting?
In metal casting, a mold is a precisely formed hollow cavity that defines the external shape and key features of a metal part. During the casting process, molten metal is introduced into this cavity, where it fills the mold, cools, and solidifies. Once solidification is complete, the mold is opened or broken away, and the finished metal casting is removed.
Metal casting itself is a manufacturing process in which metal is heated until it becomes liquid and is then poured or forced into a mold. The metal flows into the mold cavity, takes the exact shape of the cavity as it solidifies, and forms a near-net-shape component. After cooling, the solid metal part is ejected or extracted from the mold, completing the casting cycle.
While this basic principle applies to all casting processes, there are many variations. The most important variables include the mold material (such as sand, ceramic, wax-based shells, or metal molds) and the method used to deliver the molten metal, which may involve gravity pouring, pressure die casting, vacuum-assisted casting, or centrifugal casting. Each variation affects surface finish, dimensional accuracy, cooling behavior, and production efficiency.
Regardless of the specific casting method used, molds must meet several critical engineering requirements:
- Withstand high temperatures without degrading or deforming when exposed to molten metal
- Maintain dimensional accuracy to ensure the final casting meets design specifications
- Allow controlled metal flow and cooling, minimizing defects such as porosity, shrinkage, or incomplete filling
- Release the casting without damage, either through mold separation or mold destruction
As a result, the way a mold is designed and manufactured depends on the casting method, the metal type, part geometry, and required production volume.
2. Common Types of Molds Used in Metal Casting
Before learning how to make molds, it is important to understand the main mold categories used in metal casting.
Sand Molds
- Made from silica sand mixed with binders
- Typically single-use
- Widely used for iron, aluminum, and steel castings
- Cost-effective for low to medium volumes
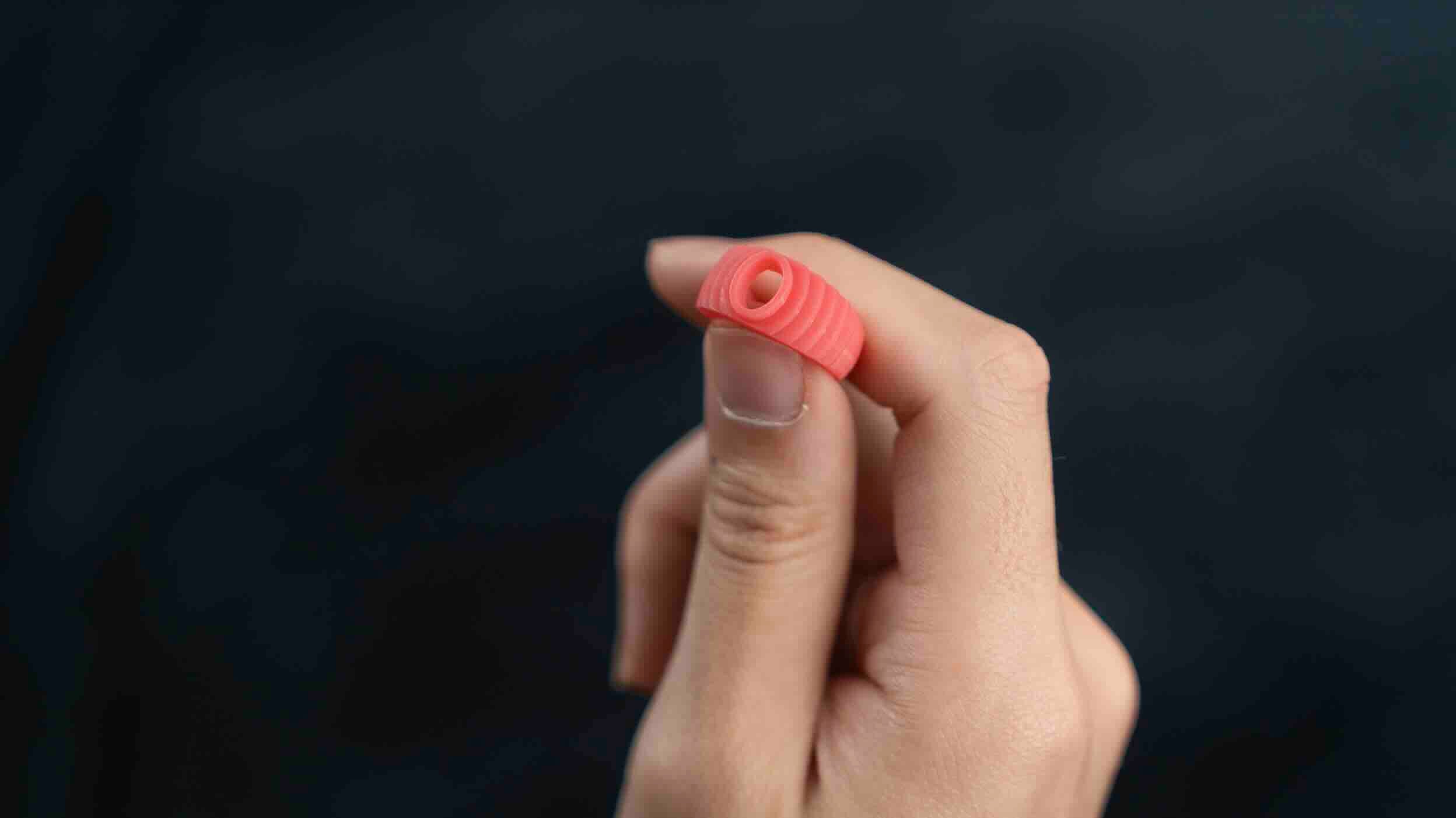
Investment Casting Molds (Lost Wax Casting)
- Created using wax patterns and ceramic shells
- Very high dimensional accuracy and surface finish
- Common in jewelry, aerospace, and precision components
Permanent Metal Molds
- Made from steel or cast iron
- Reusable for high-volume production
- Common for aluminum and magnesium casting
3D Printed Molds and Patterns
- Use wax 3D printing to create patterns or sacrificial molds
- Enable complex geometries and fast iteration
- Increasingly used in prototyping and custom casting
3. How to Make a Sand Mold for Metal Casting
Sand molding is one of the most accessible and widely used casting methods.
Step-by-Step Sand Mold Making Process
-
Create a Pattern
The pattern is a solid replica of the final part, typically made from wood, plastic, or 3D printed resin. -
Prepare the Sand Mixture
Foundry sand is mixed with clay or chemical binders to achieve proper strength and permeability. -
Pack the Sand Around the Pattern
The pattern is placed in a molding box (flask), and sand is compacted around it. -
Remove the Pattern
The pattern is carefully removed, leaving a cavity that matches the desired part shape. -
Add Gating and Risers
Channels are created to allow molten metal to flow into the mold and gases to escape. -
Close the Mold
The mold halves are aligned and clamped together, ready for pouring.
Sand molds are ideal for large parts and short production runs, though surface finish is relatively rough compared to other methods.
4. How to Make Investment Casting Molds (Lost Wax Casting)
Investment casting is one of the most precise methods for metal casting.
Step-by-Step Investment Casting Mold Process
- Create a wax pattern
- Assemble the wax tree
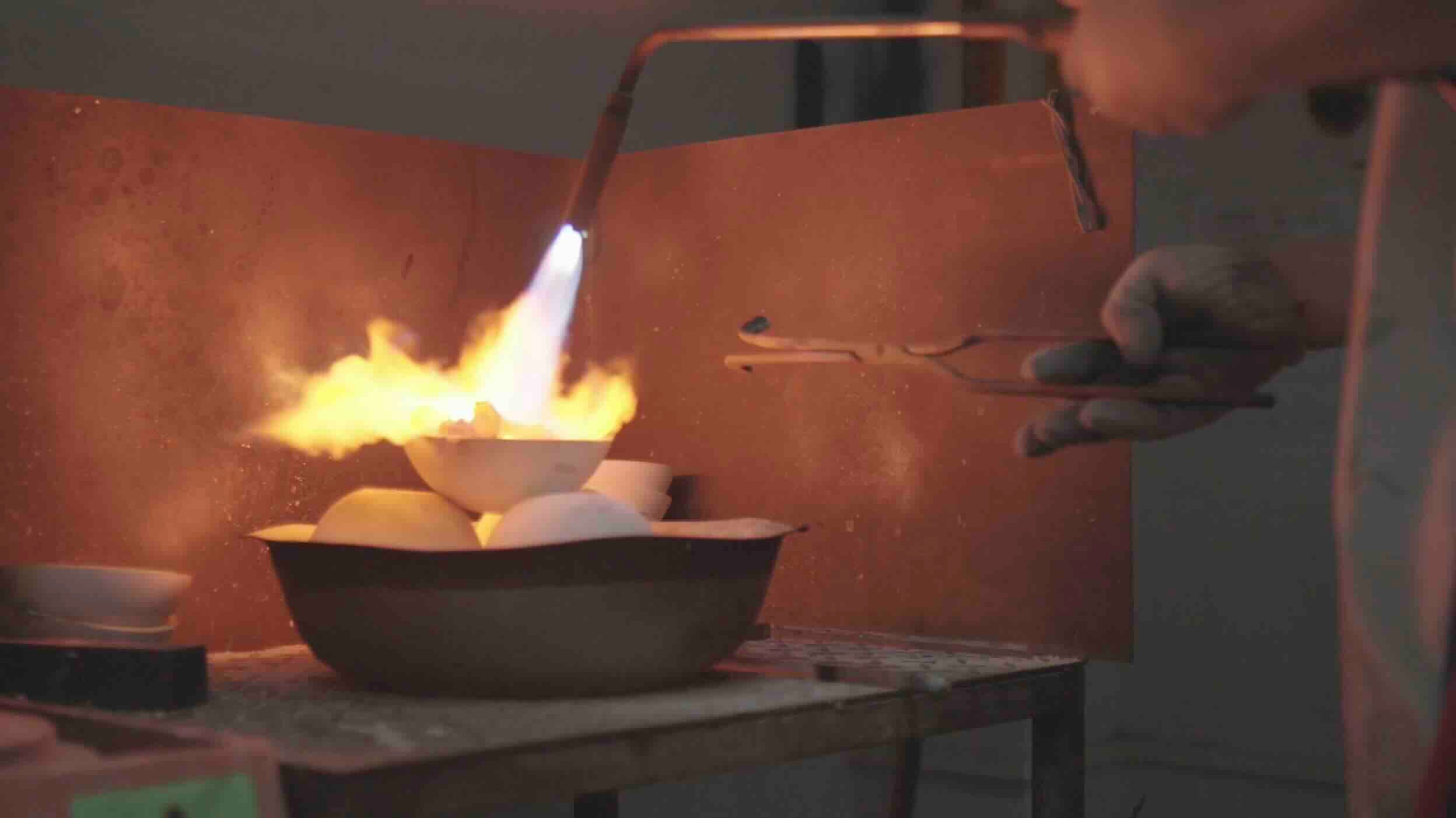
- Build the ceramic shell
- Dewax the mold
- Fire the mold
- Pour the molten metal
- Break the shell
Investment casting produces excellent surface finish, tight tolerances, and complex geometry, making it ideal for jewelry, medical, and aerospace parts.
5. How to Make Permanent Metal Molds
Permanent molds are used for high-volume, repeatable casting.
Basic Permanent Mold Manufacturing Process
- Design the mold
- Machine the mold using CNC
- Apply mold coatings
- Preheat the mold
Permanent molds offer excellent consistency but require high upfront investment.
6. Using Wax 3D Printing to Make Molds for Metal Casting
3D printing has transformed how molds and patterns are made.
Common 3D Printing Approaches
- 3D printed patterns for sand casting
- Wax 3D printed models for investment casting
- Direct 3D printed sand molds using binder jetting
Advantages of 3D Printing for Mold Making
- Rapid design iteration
- Complex internal geometries
- Reduced tooling cost
- Ideal for prototypes and small batches
7. Comparison of Mold-Making Methods for Metal Casting
| Mold Type | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Sand Molds | Low cost, flexible, suitable for large parts | Rough surface finish, lower accuracy |
| Investment Casting | High precision, excellent surface finish | Higher cost, longer process |
| Permanent Metal Molds | High repeatability, fast production | High tooling cost, limited geometry |
| 3D Printed Molds/Patterns | Fast iteration, complex shapes | Not ideal for mass production |
Conclusion: Making the Right Mold Is Key to Successful Metal Casting
Understanding how to make molds for metal casting is essential for producing high-quality cast metal parts. Whether using sand molds, investment casting, permanent molds, or modern 3D printing techniques, the mold-making process determines the final part’s accuracy, strength, and surface finish.
By choosing the appropriate mold type and following proven engineering practices, manufacturers can achieve reliable and repeatable casting results.